LemonStand Version 1 Has Been Discontinued
This documentation is for LemonStand Version 1. LemonStand is now offered as a cloud-based eCommerce platform.
You can try the new LemonStand and learn about upgrading here.
How to Manage Multiple Tax Classes
Managing multiple taxes
For some jurisdictions you may need to apply more than one tax to a same order item - for example a federal and provincial tax. LemonStand allows to apply up to 2 taxes to the same order item. To define multiple tax classes you need to specify different Priority and Tax Name values on the Rates tab. For example, if you need to apply a federal tax (say GST) to all customers from Canada and also a provincial tax (PST in this example) for customers from British Columbia you can use the following tax configuration:
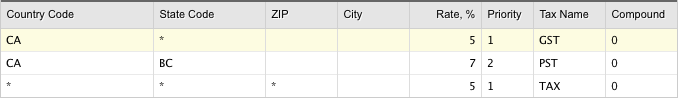
Note that we specified value 2 in the Priority column for the PST tax. When LemonStand scans the Rates table, it applies taxes with different priorities independently. That is why it is valid to specify the state-specific PST tax after the country-wide GST tax. As they have different priorities, LemonStand will first find the GST tax and after that it will scan the table again, to check whether there are taxes with other priority defined. And then it will find the PST tax.
The value in the Compound column determines whether the tax should be additive or compound (stacked). Amounts for additive taxes are calculated using the following expression:
additive tax amount = subtotal * tax_rate/100.
On the other hand, compound taxes are calculated using the following expression:
compound tax amount = (subtotal + additive tax amount) * tax_rate/100.
Thus, compound taxes use a sum of a subtotal and additive tax value as an input. In order to make the PST tax compound, you need to specify 1 in the Compound column:
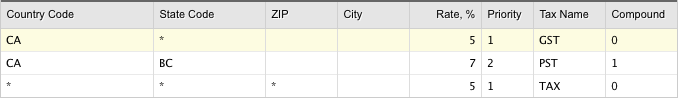
It does not matter what order you define additive and compound taxes in, additive taxes will always be applied before compound taxes.
Previous: Managing tax classes
Return to Managing tax classes
