LemonStand Version 1 Has Been Discontinued
This documentation is for LemonStand Version 1. LemonStand is now offered as a cloud-based eCommerce platform.
You can try the new LemonStand and learn about upgrading here.
Guide to Build a Simple LemonStand Module
A simplest LemonStand module should contain at least one PHP class - the module information class. The file script must be placed into the module classes directory. Also, any module should contain the updates directory, with a module version information file (version.dat) inside. Thus, a simplest module structure is:
module
-- classes
---- module_information_class.php
-- updates
---- version.dat
In this guide we will be building a blog module on behalf of some ABC company. We will not complete the module, but you should get the idea of building modules in LemonStand.
Creating the module directories
We need to create required directories and files for the blog module. As it is recommended by the naming conventions described in the Developing LemonStand modules article, the module directory name should have a prefix, matching the company name. For our case a suitable directory name is abcblog. We will be using this name as a prefix for all module class names. Now we can create the following directories in the LemonStand modules directory:
abcblog
-- classes
-- updates
Creating the module information class
A module information class is a PHP class which provides information about a module. In a simplest case a module information class should return a module name, description and a vendor (developer) name. In more complicated cases the module information class could return information about module-specific tabs in the Administration Area, module-specific user permissions, Settings page elements, dashboard indicators and reports and many other things. All these features will be described in corresponding sections of this guide.
A module information class should have a name in following the following format: [module identifier]_Module. The "Module" ending is required. In our case the class name should be AbcBlog_Module and a corresponding file name should be abcblog_module.php. We can add this file to the classes directory of our module:
abcblog
-- classes
---- abcblog_module.php
-- updates
The abcblog_module.php script should contain a definition of the module information class. Module information classes should extend the Core_ModuleBase class. This class is defined in the modules/core/classes/core_modulebase.php script. It contains all possible methods which could be defined in a LemonStand module information class. Declaration of the ABC Blog module information class:
<?php
class AbcBlog_Module extends Core_ModuleBase
{
}
?>
Only one method of the base (Core_ModuleBase) class must be overridden - the createModuleInfo() method. Other methods could be overridden only if needed. The createModuleInfo() method must return an instance of the Core_ModuleInfo class. This is a very simple class which contains module description. The class constructor accepts the following parameters: module name, description, author name and a website name (the website name parameter is optional). To complete our module information class implementation, we need to implement the createModuleInfo() method:
<?php
class AbcBlog_Module extends Core_ModuleBase
{
/**
* Creates the module information object
* @return Core_ModuleInfo
*/
protected function createModuleInfo()
{
return new Core_ModuleInfo(
"ABC Blog",
"Adds blog features to a store",
"ABC Company" );
}
}
?>In order to make sure that the module has been recognized by LemonStand, you can go to the System/Modules & Updates page and find the module in the module list.
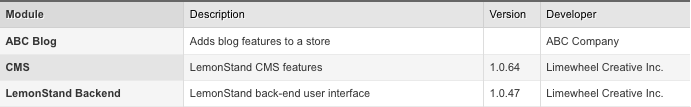
As you can see, the Version column in the module list is empty, because the version information file does not exist in our blog module.
Creating a module version information file
The module updates directory should contain the version.dat file. The version.dat file contains module versions and descriptions in the following format:
#1 Module initialization #2 Added the blog posts table #3 Added the commenting feature
Version number and version description should be delimited with a space. Tabulation symbol is not allowed.
Each time when you change something in your module, you will need to add a line to the version.dat file. You should not delete lines from the file - just add new lines. The number after the # symbol identifies a version number. After the version number there should be a space and a version description string. Each version number could have a corresponding database update script. Please read the Creating and updating database tables article for details.
For our blog module we will add only a single line to the version.dat file:
#1 Module initialization
The screenshot displays the final file structure of our blog module:
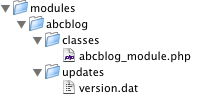
If you refresh the System/Modules & Updates page at this point, you will see that the Version column is still empty.
LemonStand reads and applies module updates only in two cases: when somebody logs into the Administration Area and during the Software Update session
As you develop the module locally, the simplest way to apply updates is to log out and then log into the Administration Area. After that you can open the module list page and make sure that our blog module has been updated and now its value is 1.0.1.
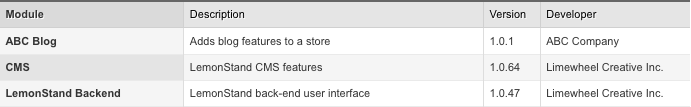
As you can see the module version number consists of three numbers - major_version.minor_version.build_number. LemonStand considers the version number specified in the version.dat file as a module build number and by by default it assigns 1 and 0 values to the major and minor version number parts. But you can specify a specific version string in the version.dat file, using the following format:
#302|2.1.3 Added some great features
In this case the build number is 302, but the version string is 2.1.3. LemonStand will display the 2.1.3 value in the Version column of the module list. You should always increase the build number in the version.dat file, independently from a version string corresponding a build.
Conclusion
That is all what you need in order to create a simplest module, which does not add any new functions to LemonStand. You can download the blog module ZIP archive here.
Next: Programming Module CMS Actions
Previous: Understanding LemonStand Modules
Return to Understanding LemonStand Modules
